What Happens to our body in spring
Hello everyone we wish you health, happiness and ideal abundance for your families and friends. On week 260 we are sharing spring according to Chinese medicine. A very well researched post, enjoy and don’t forget to share and like, it helps us to keep going.
According to: http://www.itmonline.org
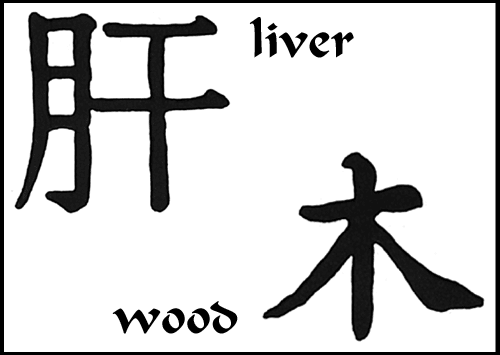
The liver is associated with wood. Wood qi is characterized by its upward momentum and its innate desire to be straight. As long as the flow of liver qi is not impeded, the blood vessels will remain open and unobstructed.
The liver is the organ that is in charge of storing blood. It also commands the ministerial fire (xiang huo). If there is sufficient blood, this fire will be warm but not fierce. As a result, the blood can circulate smoothly through the body’s three burning spaces; it will reach the pores, and every single place in the body will benefit from its warming and nourishing function.
Liver and spleen function together by assisting each other. However, people are always quick to point out that an excess of liver wood can injure the spleen earth, and thus have a detrimental affect on the proper digestion of food. But nobody seems to pay attention to the fact that a weak liver cannot circulate the spleen qi and thereby also cause maldigestion. Below, the liver connects to the Sea of Qi [lower dantian, associated with the kidney], which means that the liver is closely associated with the body’s ministerial fire. It can utilize the power of this fire to produce earth. The food which enters the spleen and stomach relies on this power to be ‘cooked.’ This is what is meant by saying that the liver and the spleen function by assisting each other.
The liver relies entirely on kidney water to sustain it, on blood to moisten it, on lung metal’s clear nature and descending function to keep it in check, and on the generosity of the middle palace’s earth qi to nourish it.
The eyes represent the orifices of the liver.
When a person closes his/her eyes and falls asleep, the blood returns to the liver. From there it is transmitted to the eyes, and the ability to see results from this. When a person sleeps, now, the nameless fire within grows dim in order to revitalize. Although it may be impossible to refrain from sleeping altogether, it is advisable not to just let this energy dissipate for the mere sake of falling into a slumber.
Insomnia caused by a cold deficiency pattern of the gallbladder is accompanied by symptoms of restless thought and a sensation of extreme mental weariness. Excess heat in the liver will typically cause a person to sleep too much, resulting in the mirror of intelligence gathering dust and a deterioration of the root of good health. None of these conditions, obviously, are the result of proper nourishing of the liver and gallbladder nor an appropriate way of subduing the sleep issues.
The essence of sleep, after all, is the soul of the body. If you can manage to sleep without over doing it , then the master mind will be bright and alert. Not only will your shen qi be flowing freely and purely, but you will also not be disturbed by dreams. Every time you are overcome by a craving for sleep, blood rushes to the heart and the original shen is forced to leave its abode.
Spring is the liver time.
‘The three months of spring are the period of commencement; heaven and earth are born, and all living things are flourishing. Get up early in the morning, walk around in the courtyard, loosen your hair and relax your body. By doing so you will generate mental strength and act in harmony with the qi of spring, thus following the way of nourishing life. If you live contrary to this principle, you will harm your liver.’ Everybody should be aware of this basic principle.
Emotions such as anger, embarrassment, or unexpected joy can also increase blood flow, causing the ears and face to turn red. In situations when less blood is needed, it is “stored in the liver,” which thus assumes a warehouse-like function. The actual storage of blood is done in the penetrating vessel, one of the eight extraordinary vessels that extends from the lower dantian to the head; this vessel is often considered to be part of the liver network. The liver is best compared to a managing clerk, who moves goods in and out of the warehouse as they are needed.
Just as important is the liver’s function of maintaining a smooth and uninterrupted flow of virtually all body substances (including qi, blood, jing, and liquids and humors). Proper coursing and draining, or lack thereof, is mostly reflected in the relation of emotions to qi and blood circulation and to the influence of the liver on digestive system functions:
Emotional aspect: the ancient Chinese observed that human emotions are largely governed by the heart network. However, they also concluded that mental well-being or various shades of depression have an association with the coursing and draining function of the liver. Only if the liver carries this task out properly can the body’s qi and blood flow unobstructed, and thus facilitate a feeling of ease, harmony, and peace. If for some reason the liver fails to maintain this state, depression (of liver qi) or pathological rising (of liver yang) may result. As the Qing Dynasty classic, A Treatise on Blood Disorders (Xue Zheng Lun), states: “The liver is classified as wood; wood qi is characterized by its determination to go straight to where it wants to go to; if it is not blocked or suppressed, the movement in the vessels will be smooth.”
Digestive aspect: since this moving function of the liver regulates the qi flow in the entire body, it influences the dynamics of the other organ networks, particularly the neighboring digestive systems. It assists the upward and downward flows of the spleen/stomach system (the stomach is to move the food mass downward, the spleen is to move the extracted qi upward), passes bile into the intestines, helps to transport food essence, and aids the unobstructed movement and metabolism of water. The Treatise on Blood Disorders says “Coursing and draining is an integral part of liver nature. Once food qi enters the stomach, it is entirely up to the liver wood to course and drain it. Only if this process is intact will grain and water transform properly.”
According to traditional concepts, male physiology is mostly based on qi (yang), while female physiology is primarily based on blood (yin). Males tend to have an abundance of qi that they can afford to spend freely, while females have an abundance of blood that they can give away freely (as becomes evident from the menstrual bleeding). Liver function, therefore, has great influence over an important part of female physiology-menstruation.
The penetrating vessel and the conception vessel, are two pathways linked to the liver that are intimately involved with the transportation of blood. The penetrating vessel, above compared to a warehouse, is also called the Sea of Blood; and the conception vessel, as the name indicates, is credited with the function of nourishing the uterus and the fetus. Both the conception vessel and the penetrating vessel belong to the category of the eight extraordinary vessels. Both these vessels are involved in the liver’s ability to store blood; they set out from the uterus, and are also closely linked with the kidney channel.
The When one’s circadian rhythm is disrupted, sleeping and eating patterns can run amok connect the muscles to the bones. In accordance with the characteristics of the liver, they facilitate smooth and continuous movement. Because of this basic concept, some scholars have recently included the nerves. The proper functioning of the tendons relies entirely on their nourishment by liver blood.
The nails are considered the surplus of the tendons: as such, they are an exterior manifestation of the general quality of the tendons, and thus, liver blood within. Dry and brittle or extremely pale nail beds always indicate a poor quality of liver blood, while pink nailbeds and firm nails indicate a healthy state of liver blood.
Hair is also associated with the liver blood: it is called the “surplus of the blood” (xue yu). The rich liver blood of females is expressed in lush, long, and fast growing hair on the head; males have more facial and body hair, which is governed by the qi organ, lung. Dry and brittle hair can be an indication of liver blood deficiency, while hair that suddenly falls out (alopecia) is usually because of both deficiency of blood and impeded flow of liver blood to the head, usually due to sudden emotional trauma.
The eyes are nourished by the essence of all five organ networks, and thus differentiated into five organ specific zones which may reveal important diagnostic information. The eyes as a whole, however, represent the opening of the liver, and are thus considered to be more closely linked to the liver than to any of the other organ networks. “Liver qi communicates with the eyes,” states the Neijing, “and if the liver functions harmoniously, the eyes can differentiate the five essential colors….If the liver receives blood, we can see. The liver channel branches out to the eyes. Both liver qi and liver blood flood the eyes to maintain proper eyesight. A person’s eyesight may therefore also serve as an indicator for liver function.
Just as trees (wood) tend to unrelentingly pursue their upward quest for the light, the liver represents the innate will of the body/mind to spread outward. Just like qi and blood have to spread within the body to ensure physical survival, human shen needs to spread freely through the social environment to guarantee an uninhibited passage through life. Individuals with strong liver qi and blood are usually excellent strategic planners and decision makers: they know how to spread themselves into the world. Due to these qualities, they often make outstanding business managers. If, however, this tough and determined spreading nature of the liver is not in a state of harmonious balance with the softer side of liver wood-ease, smoothness, flexibility-the wood-endangering state of rigidity arises.
The Liver Loses Its Ability to Course and Drain: if qi gets stuck, the inhibited coursing action of liver qi immediately manifests in the form of mental and emotional symptoms; depression, sensation of emotional pain, or crying are typical examples. If liver qi flares up and upsets the harmonious interplay between body and mind, outbursts of anger, or pain and distention in the sides of the chest may result.Typical signs of a liver qi disorder implicating the neighboring spleen/stomach system are belching, regurgitation of stomach acid, vomiting, and diarrhea.
Liver Disharmony Reflecting on the Emotions and Mental Activities: a deficiency of liver qi typically causes a person to be indecisive and adrift, with a marked inability to plan ahead effectively. If gallbladder qi is deficient, the person will be fearful, have a panicky disposition, and have difficulty making decisions.primary symptoms are tendency to get depressed; frequent sighing; impatient disposition and temper outbreaks; sensations of stuffiness; fullness or congestion in the chest, intercostal, or subcostal regions. Secondary symptoms include obstructed bowel movements; dry and distended eyes; feeling of something being stuck in the throat; self-doubts and crying; pain (especially intercostal and abdominal) that is characterized by moving, pulling, or penetrating sensations; in females; premenstrual breast distention; menstrual cramping and irregular menstruation. The tongue typically presents with a reddish body (especially at the sides) and a thin coating; the pulse tends to be wiry.
LIVER YIN DEFICIENCY herbs:peony (baishao), lycium fruit (gouqizi), ligustrum (nuzhenzi), gelatin (ejiao), tang-kuei (danggui), rehmannia (dihuang), cornus (shanzhuyu), ho-shou-wu (heshouwu), turtle shell (biejia), zizyphus (suanzaoren), biota (baiziren).
LIVER BLOOD DEFICIENCY Representative Herbs: tang-kuei (danggui), peony (baishao), gelatin (ejiao), ligustrum (nuzhenzi), cornus (shanzhuyu), cnidium (chuanxiong), zizyphus (suanzaoren), millettia (jixueteng).
Representative Formulas: Tang-kuei Four Combination (Siwu Tang); Tonify the Liver Decoction (Bugan Tang); Linking Decoction (Yiguan Jian) minus melia (chuanlianzi) plus peony (baishao).
Before making any desitions in suplements please consult your Health provider and a Certified Acupuncture practicioner.
Time for the organs and meridians
from: http://www.drterrywillard.com
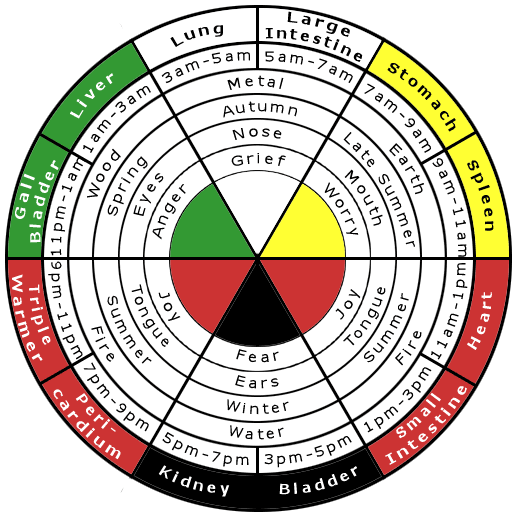
According Circadian rhythms (Often referred to as the “body clock”, the circadian rhythm is a 24-hour cycle that tells our bodies when to sleep and regulates many other physiological processes. This internal body clock is affected by environmental cues, like sunlight and temperature. When one’s circadian rhythm is disrupted, sleeping and eating patterns can run amok) and the TCM (Traditional Chinese Medicine) meridian clock can greatly influence our body and our mind. These rhythms tell a practitioner a lot about a person’s general health and challenges .One of the easiest places to see this is with sleep patterns. Many people complain about always waking at the same time through the night.
Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) meridian clock could give us great clues. If a person always wakes at 2:00 am, this is in the time of the Liver.
Not to be concerned, this doesn’t mean you have a serious liver problem; the word Liver is partly a translation issue.
The acupuncture meridians are an energetic system, or a kind of ‘electrical system,’ of our energy patterns. These meridians have often been said to be rivers of energy called Qi (pronounced Chee). The meridians might be in our body, but there is no specific anatomical part that makes them up. They are more like radio waves. The organ associated with a meridian, in this case the liver, is not the cause of the meridian; the organ is more or less a physical artifact, of the Qi of the meridian. Simply, the Liver meridian’s energy pattern deals with much more than the physical organ of the liver. In Chinese Medicine there are 14 major meridians that conduct the flow of Qi throughout the body. Twelve of these meridians make up the 24-hour clock, with 2 hours each. The energy is constantly flowing through all of these meridians throughout the 24 hours, with each meridian having a 2-hour period of time as the primary meridian.s resistance or blockages (like stress) that reduce the flow of energy. This resistance also causes imbalance in the flow between meridians.
By looking back at the meridian clock, you may find some clues as to what is going on. Remember, the body never lies.
Each one of the meridians also has certain responsibilities. Following is a basic list of these attributes:
- Stomach – Nourishment of others; nourishment from outside
- Spleen – Nourishment of self in every way
- Heart – Connection to your spirit; circulation of Qi (energy); heart and mind working as one
- Small Intestine – Communication (speaking, listening); perception; truth
- Bladder – When to use our resources; being controlling
- Kidney – Reproduction and creating things in life; our resources
- Pericardium (aka Sex/Circulation) – Intimate relationships; protecting your heart; healthy boundaries
- Triple Heater – Non-intimate relationships; social aspects
- Gall Bladder – Determination and decision making; action
- Liver – Internal plans; the vision for life
- Lung – Barrier (skin) to the outside world; understanding what is of true value
- Large Intestine – Letting go of impurities (of emotions and beliefs, past experiences) ; holding on to what is of value
Recipes for the liver
from: http://www.tcmworld.org/
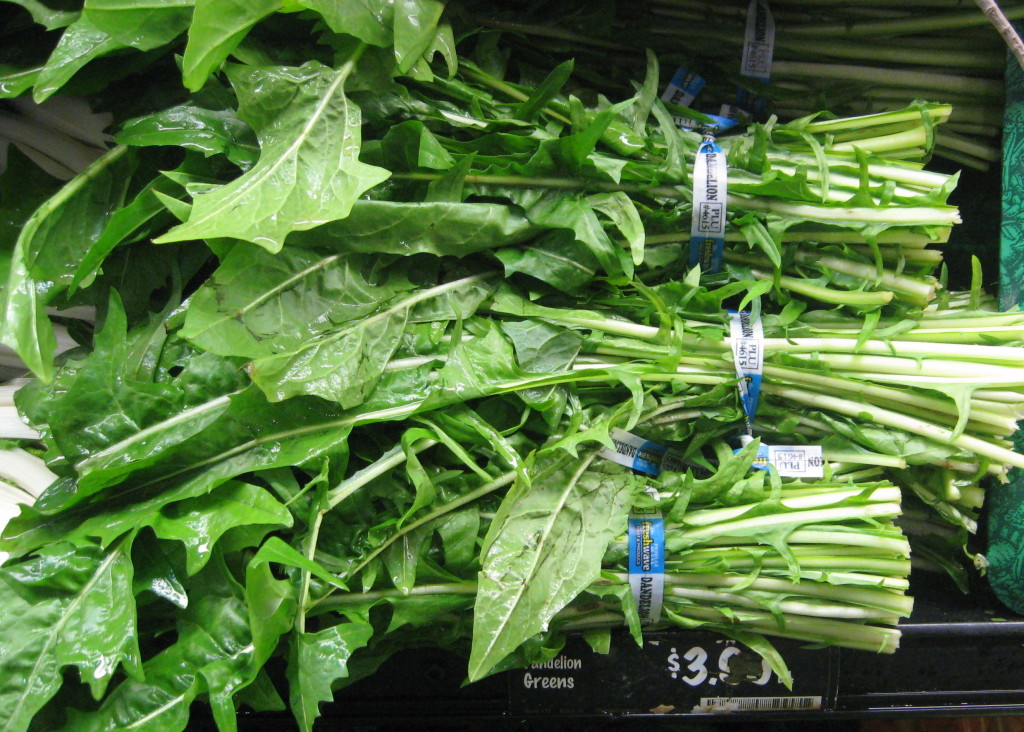
IRMA’S DANDELION DELIGHT
Dandelion greens are ideal for supporting Liver health and for clearing toxic heat out of body and blood. Scallions and garlic also help to support Liver health. Try adding pine nuts or black sesame seeds to give support to the Liver’s mother, the Kidney. Adding spicy chili black bean sauce and sugar will help cut some of the natural bitterness of the dandelion greens.
Ingredients
• 2 cups of washed and chopped (2 inch pieces) dandelion greens
• 1 scallion
• 1 clove of garlic, diced (optional)
• Grapeseed oil for cooking
• Salt (to taste)
• Cooking wine (Chinese rice cooking wine or sherry is nice)
• Mushroom powder (optional)
• Chili black bean sauce (optional, also can use oyster, teriyaki, garlic, etc.)
• Honey (to taste)
• Toasted pine nuts (optional)
• Toasted black sesame seeds (optional)
Preparation
Cut one scallion into 2-inch pieces. Heat a wok with grapeseed oil until very hot. Add a small pinch of salt. Add the scallion and garlic and cook, stirring, for about 10 seconds. Add greens. Sauté lightly, adding a splash of water if too dry. Add more salt, mushroom powder, and Honey (to balance the bitterness), to taste. Add a splash of cooking wine or stir-fry sauce to taste. Toss with sesame seeds or pine nuts before serving.
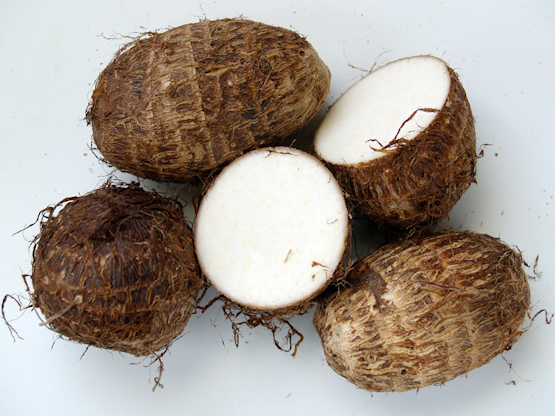
TEN MINUTE TARO AND LEEK SOUP
Taro root is harvested in the fall and is great to promote a healthy digestive system.The leeks will support your Liver while seaweed will help the Kidney.
Ingredients
• 1 cup of diced taro root
• 3/4 cup of leek, sliced thin
• Handful of dried seaweed
• 1/2 teaspoon of olive oil
• Salt to taste
• 1/4 teaspoon of sesame seed oil (optional)
Preparation
Bring 2 quarts of water to a boil. Add taro root, leek, seaweed and salt. Allow mixture to boil for ten minutes. Add olive oil and let boil one additional minute. If you like the flavor of sesame oil, add a dash just before serving. Tip: make sure you have enough water boiling to allow the taro root space to move while cooking. Do not let the taro root get mushy.
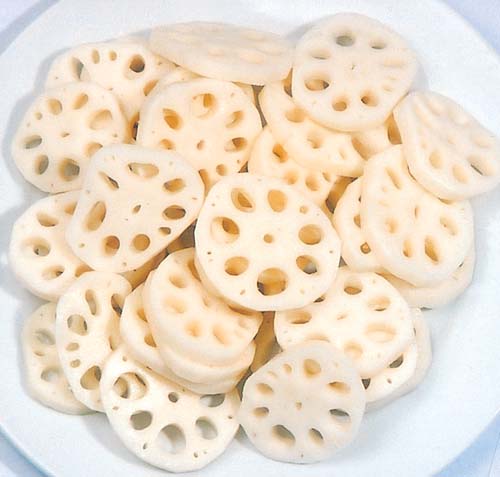
CRUNCHY LOTUS ROOT
This delicious and crunchy food has been used for thousands of years to support Lung function as well as Liver function. Sautéed, juiced, or ground for tea, the lotus root is a great addition to your diet, especially in autumn.
Ingredients
• 1 lotus root
• 1 scallion
• Oil
• Salt
• Honey
• Fish sauce
• Chinese rice wine
• Water as needed
Preparation
Peel the lotus root, cut in half lengthwise, and then slice thinly. Chop the scallion in 1-inch pieces, separating the green from the white portions. Heat the wok well, then add the oil and continue to heat. Add a pinch of salt and the white portion of the scallion. Stir in the lotus root and continue to cook for about 1 minute. Add the ½ teaspoon of Honey (or to taste), a splash of fish sauce, and toss well for 1 minute. Finish off by adding a splash of rice wine, toss and serve warm.
Some great products for spring. Just click on the image to purchase.
Green Tea Sampler
A chance to broaden your discovery with the very best of green teas. Each sample makes about 8-10 cups of tea. This set includes: